Cohort Study and Biobank
Cohort Studies
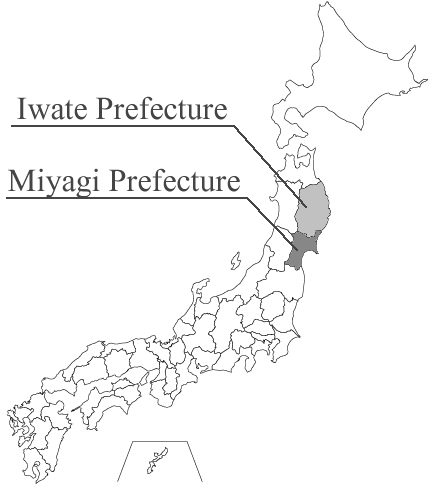
To study how genetic factors and environmental factors affect disease risk, two large-scale prospective studies, the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Community-Based Cohort Study (TMM CommCohort Study) and the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study (TMM BirThree Cohort Study), are ongoing in Miyagi and Iwate Prefectures in Japan.
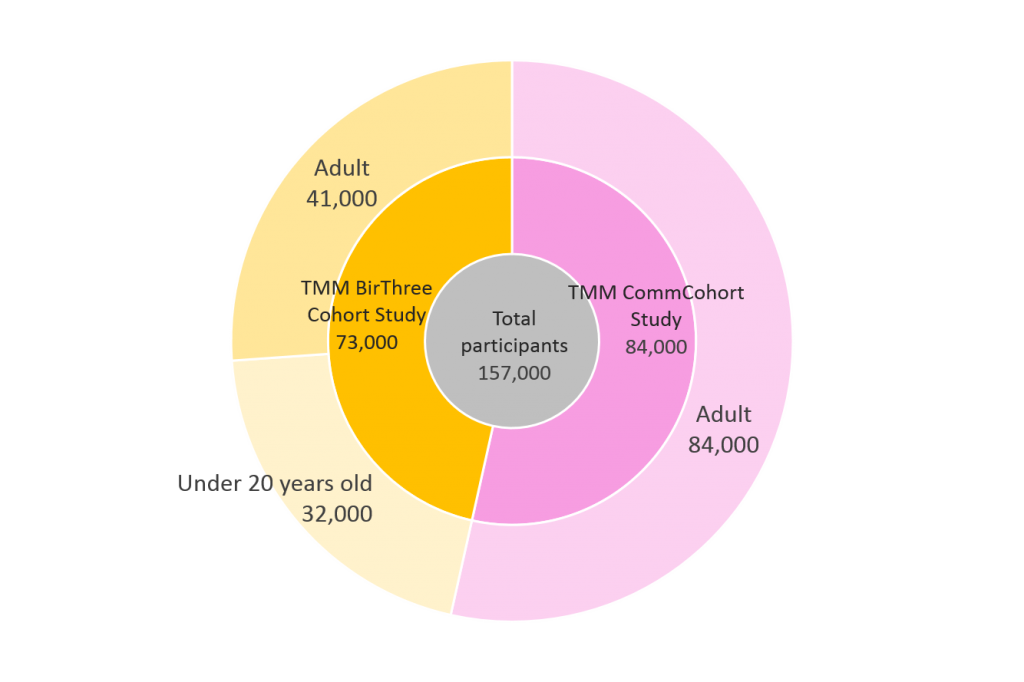
From 2013, the commencement of the cohort studies, till 2017, ToMMo has successfully recruited more than 150,000 participants to undertake the baseline assessment. This involved collection of biospecimens from the participants, including serum, plasma, mononuclear cells and urine; along with conducting questionnaires regarding their lifestyle and medical history. The detailed health survey was conducted in the community support centers, located in seven locations across Miyagi Prefecture.
In the four years between the baseline and secondary assessments, participants were mailed an annual survey as part of the follow up of their health. In order to grasp better understanding of the long term changes in health conditions, secondary and tertiary assessments were established as part of a follow-up study on participants whom undertook the baseline assessment. Participants were requested to visit their closest community support center once every three to five years for biospecimen collection and subsequent analyses.
As of July 2021, ToMMo has officially begun the tertiary assessment stage of the cohort studies. The tertiary assessment resembles closely to that of the secondary assessment, however not only does it monitor the previous health parameters of interest, but additionally the participants’ memory/thinking abilities. As the tertiary assessment brings the cohort studies to over the ten-year mark, ToMMo is interested in seeing the individual differences in health parameters that changes with age. In doing so, ToMMo believes that this data can allow us to be closer towards the attainment of personalized healthcare, and thus, a healthier population with greater longevity.
Detail of cohort studies
| Name of cohort study | Type | Recruitment target |
| TMM CommCohort Study | Population-based cohort | Local residents who are 20 years old or older |
| TMM BirThree Cohort Study | Family-based cohort, Birth and Three-generation cohort |
Expectant mothers and their family |
- Community-Based Cohort Study (TMM CommCohort Study)
- Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study (TMM BirThree Cohort Study)
Number of cohort study participants
Related information
Return of Genomic Results to Cohort Study Participants
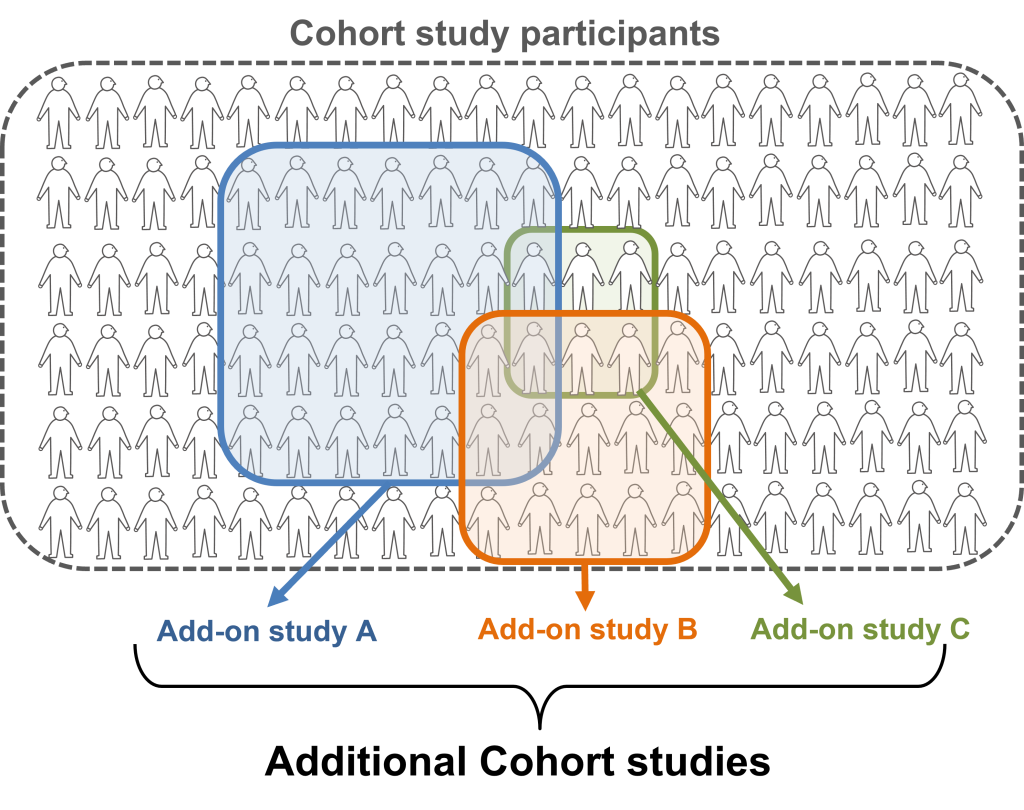
Additional Cohort Studies (add-on study)
The participants of the TMM CommCohort Study and TMM BirThree Cohort Study were asked to participate in further cohort studies, including but not limited to ‘The Brain-MRI Project’. This study implements the use of MRI technology in studying different aspects of the human brain, in combination with cognitive psychology testing. The purpose of this study is to better understand how the constitution of the brain and one’s lifestyle habits can affect the cognitive function of the brain. In doing so, ToMMo aims to provide information that can allow us to come up with ways to maintain a healthy brain and cognition throughout one’s lifetime.
Another study implemented by ToMMo and OMRON Healthcare Co., Ltd. involves studying the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio of participants. ToMMo and OMRON believe that one can create and maintain a healthy lifestyle from their own home. Using point-of-care testing devices distributed from OMRON Healthcare, participants were able to take multiple measurements of the sodium and potassium levels in their urine at various points in during their day. The results revealed that multiple measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio demonstrated a more sensitive association with hypertension than single measurements.
The above additional cohort studies are only two, amongst many, cohort studies that ToMMo has implemented throughout the past decade. The data obtained from a variety of additional cohort studies has and continues to provide additional data that makes ToMMo’s biobank resources richer. In doing so, we become one step closer towards achieving a more personalized healthcare approach.
The scheme of additional cohort studies
The subjects of additional cohort studies are a part of cohort study participants.
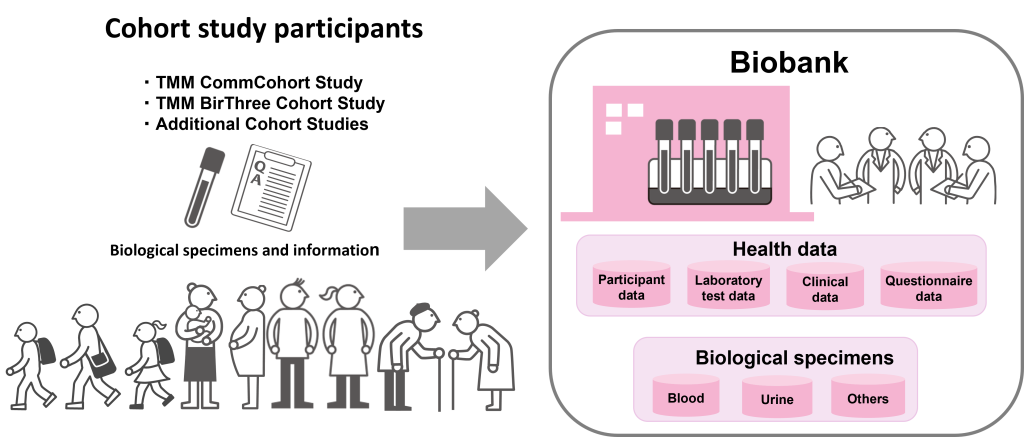
Biobank
To achieve next-generation medicine, such as personalized medicine and healthcare, we have been developing the biobank from the biological specimens of 150,000 cohort study participants. Not only are millions of high-quality biological specimens such as serum, plasma, mononuclear cells, DNA, health information, and genetic data from the cohort study participants stored with high security; basic information such as age, test information and information on lifestyle habits based on the questionnaires are also stored securely.
Our biobank integrates analytical functions and utilizes biospecimens and information of participants in an integrated manner, and hence is called an ‘Integrated Biobank’, where many researchers can utilize the data. As the years pass, biospecimens and information in the biobank accumulate. As a result, we can expect to form a biobank that covers the entire human life course, with biospecimens and information in all stages of life.
Quality Management of Biospecimens and Information
Under strict security, high quality biospecimens and information are stored in our biobank, through utilizing a system called LIMS (Laboratory Information Management System). All biospecimens are managed with barcodes, and biospecimen traceability is ensured by recordkeeping at all stages of the work process – such as, dispensation, processing and storage. Additionally, many of the work processes are automated, which ensures that human error is minimized.
Two types of storage systems are used according to the characteristics of the samples and the frequency of delivery, in order to maximized storage and operation efficiency.
In addition, an integrated database called dbTMM has been established to store the collected cohort information and sample analysis results in an integrated manner. The information is stored sequentially, beginning with the information that has been organized, and is being used by many researchers under sufficient security measures. Upon evaluation of our biobank, integrated database and the shared usage of biospecimens and information, our three sections are certified by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Related information
Publications
- The Tohoku Medical Megabank Project: Design and Mission
- Biobank Establishment and Sample Management in the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project
- Cohort Profile: Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study (TMM BirThree Cohort Study): Rationale, Progress and Perspective
Other Major Publications (cohort study)
Other Major Publications (biobank)
Press Releases
-Lengthy Screen Time Associated with Childhood Development Delays (Aug. 30, 2023)
-Spouses Really Are Together in Sickness and in Health Suggests New Study (Sep. 22, 2021)
-ToMMo completed the ToMMo Child Health Study in Miyagi Prefecture during a period of four years after the Great East Earthquake (Apr. 5, 2016)
-Depressive symptoms continue to be higher in coastal areas than in inland areas 3 years after the Great East Japan Earthquake (Mar. 16, 2016)
-Psychological Consequences Remain Profound Among Coastal Communities Devastated by the Great East Japan Earthquake (Sep. 1, 2015)
-Findings from the FY2013 Long-term community child health study (Jan. 17, 2014)
News
-New article reporting the design and results of the Brain-MRI Study was published in Journal of the Japan Medical Association (July 19, 2023)
-The article about the design and pilot study for return of genomic results in TMM cohort study was published (July 27, 2021)
-The article about study profile of The Tohoku Medical Megabank Community-Based Cohort Study was published (Aug. 31, 2020)
-The article about design and progress of oral health examinations in Tohoku Medical Megabank Project was published (June 26, 2020)
-The article about the design of Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study was published (Sep. 30, 2019)
-The number of participants for the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Birth and Three-Generation Cohort Study reached to 70,000 (Jan. 26, 2017)
-iPS cells made from cells collected through the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project (Apr. 19, 2019)
-50,000 people have participated in the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project Community-Based Cohort Study in Miyagi Prefecture (Nov. 4, 2015)
Interviews
-Interview with Dr. Tomita from the Department of Disaster Psychiatry (Oct. 8, 2014)
