Facilities and Equipment
The building for the Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization was designed for Tohoku Medical Megabank Project and the construction of that completed in 2014. It is located on the southwest corner of the Seiryo campus. The building has seismically isolated structure and some characteristics specialized for the project. Around 300 people are working in this building for establishing the genome medicine.
A virtual tour video (Japanese subtitles only) is also available.
| Floor | 7 stories (partly 5 stories) |
| Structure | Precast concrete structure (base isolation system), joint complex with the "School of Medicine, Building No.6". |
| Building area | 3425.62m2 |
| Total floor area | 18,017.67m2 |
| Major facilities | Biobank (Biospecimen Storage), MRI, NMR, Genome Analyzing System, Supercomputer System, Sendai Community Support Center |

Sendai Community Support Center
For cohort studies, we have established seven Community Support Centers in Miyagi Prefecture (Kesennuma, Osaki, lshinomaki, Tagajo, Sendai, lwanuma, and Shiraishi). The centers are equipped to handle various types of surveys after confirming consent from each individual by a Genome Medical Research Coordinator (GMRC). In Sendai, a dedicated facility for conducting health surveys with particularly for children, called Sendai Child Health Square, was opened in June 2017. Also MRI equipment has also been installed in Sendai, and MRI imaging is provided to cohort participants who have been taking health surveys in the centers and wish to do so.

Community Support Center
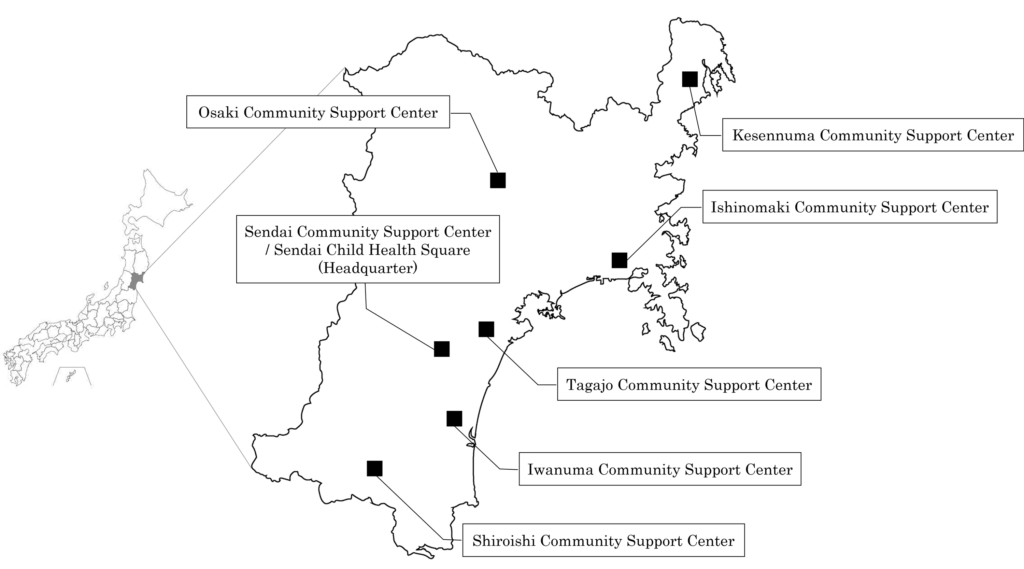
*All support centers are located in Miyagi Prefecture
*The satellite offices (assessment center same as our support center) in Iwate Prefecture are organized by Iwate Medical University Iwate Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization (IMM)
Health Survey Detail
Informed consent, blood test, body composition, grip strength test, bone density measurement, hearing test, oral health check-up, carotid ultrasound imaging, respiratory function test, ophthalmic examination, questionnaire by touch screen, electro-cardiogram, MRI, cognitive assessment.

MRI
Two dedicated 3.0 Tesla high-resolution MRI scanners have been installed in the building for the Tohoku Medical Megabank Organization. These scanners will allow us to collect data from several thousand subjects every year. We will assess brain gray and white matter volumes, white matter integrities, white matter lesions, brain perfusions, and brain vessel structures through several scanning protocols. We are investigating how daily habits or genetic factors influence the brain, its cognitive functions, and psychological conditions in order to maintain a healthy brain and good cognitive functions for life. Based on these studies, we are considering health damage such as PTSD after the disaster.
Sendai Child Health Square
The Sendai Child Health Square was established in June 2017 as a facility for conducting child health surveys to monitor the development of children. The facility is equipped to primarily survey the health of children aged 5, 10, and 16 years, who are already enrolled as participants in TMM BirThree Cohort Study, while also providing an enjoyable atmosphere for the participating children. The major equipment used for the surveys is similar to that in the Sendai Community Support Center. It is also furnished with special equipment related to child development, such as the Gazefinder (a social development evaluation system).

Supercomputer System
The supercomputer system is the data infrastructure for storing various data generated from a 150,000 people genome cohort, as well as the analysis infrastructure supporting large-scale genomic and omics analysis. As a data infrastructure, the system is equipped with a massively parallel hard disk drive that enables high-speed data analysis and storage consisting of tape libraries/object storage/optical disk libraries that can store data for a long period of time, making it the largest system in the life science field in Japan. As an analysis platform, the system is equipped with a large number of CPUs to perform large-scale genomic and omics analysis, which is essential for the construction of next-generation medicine, and enables high-speed data analysis. The system is designed to efficiently perform the analysis necessary to realize personalized healthcare while ensuring a high level of security for the diverse data from the complex biobank.


Equipment Configuration
| Compute Node(CPU) | Shared Memory | GPU Analysis Nodes | Login Node | Database Server | |
| Total nodes | 130 | 3 | 3 | 8 | 6 |
| Total CPU cores | 14,880 | 384 | 384 | 1,024 | 768 |
| Total memory size (TB) | 60 | 12 | 1.5 | 8 | 3 |
| Total GPU | - | - | 24 | - | - |
| High Performance Storage | Archive Storage |
| 55PB | 10.5PB |
Common Terminal Room
The common terminal room is equipped with several terminals that can be connected to the supercomputer system in a secure room with biometric authentication facilities. These are also dozens of remote security areas with similar function and access to the ToMMo supercomputer in Sendai from remote locations throughout Japan and the integrated database dbTMM can be used and analysis and calculations can be performed using the supercomputer.

Related Link
The Supercomputer System has been renewed! (April 2022)
Biobank (Biospecimen Storage)
The TMM biobank is one of the largest population-based biobanks in Japan that stores millions of biological specimens in state-of-the-art storage systems. Automated sample storage system can hold 4.5 million tubes which contain blood components, urine, breast milk and DNA at either -80℃ or 4℃. The system handles the specimens autonomously, minimizing the frequency of human errors and sample damage. The liquid nitrogen storage system can hold 1.3 million tubes in the vapor phase of liquid nitrogen below -180℃.
The tubes contain peripheral and cord blood mononuclear cells, along with their derivatives. The specimen-associated information is managed by the Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS).


Equipment Configuration
| Model | Temperature/Purpose of Use | Capacity | Feature |
| Brooks Biostore II | -80°C /Storage of plasma, serum, buffy coat, urine, breast milk | Around 5.9 million sample tubes in total | Fully automated loading and unloading system. Small aperture to prevent the temperature change. |
| Brooks SampleStore II | 4°C / Storage of DNA |
| Model | Capacity | Feature |
| Taiyo Nippon Sanso DR-1000AT (G)-16 |
Around 1.3 million sample tubes in total |
Automatic filling device of liquid nitrogen. Sample storage under homogenized gas phase below -180°C. |
| Chart MVE 1894R-190AF-GB |
Related Link
Sample Processing in TMM Biobank (movie)
Genome Sequence Analysis
ToMMo sequencing facility has different types of next-generation sequencers. It has an annual output capacity of more than tens of thousands of high-grade whole human genome sequences. To perform such high throughput sequencing without any sample mix-ups, highly automated experimental pipelines for sample preparations. Using not only short-read sequencers but also long-read sequencers, various types of diversities with the human genome, such as single nucleotide variants and structural variants, are analyzed. In order to sequence a whole human genome with the best quality possible, 20 to 100 times the amount of data (up to 300 billion bases) must be collected for analysis. These massive amounts of data are protected by a highly secure information network and analyzed with our supercomputer system.
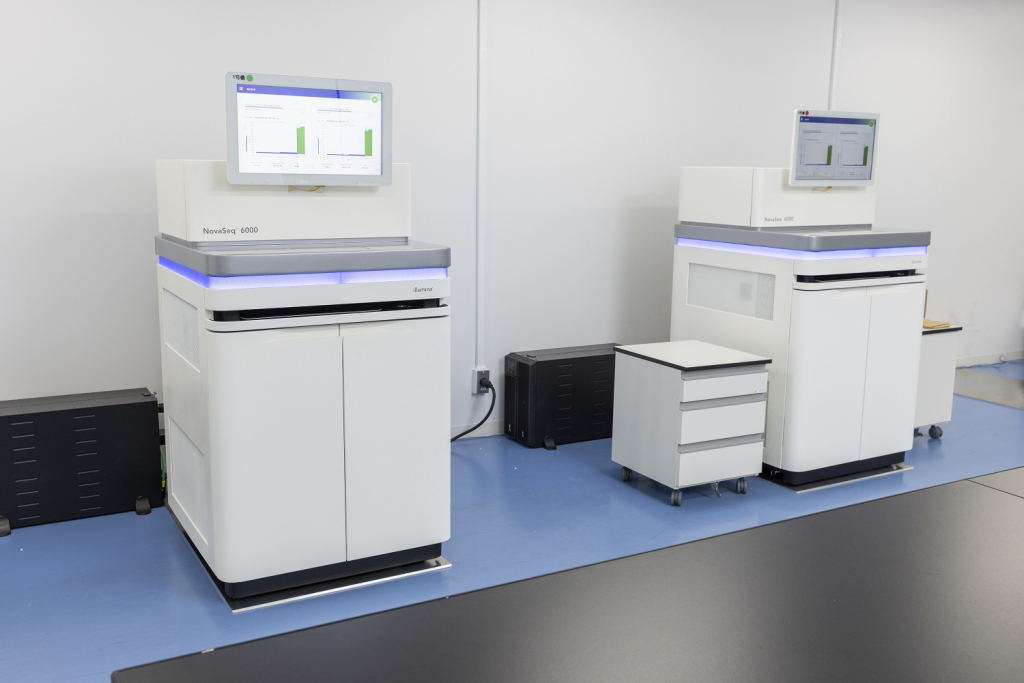

Equipment Configuration
| Model | Feature / Use |
| NovaSeq X Plus (Illumina) |
Max output:7,500 Gb / flow cell Max paired end reads:25 billion reads/run (with 20B flowcell) Max read length:150 bp×2 The whole genome sequence of 150 individuals can be analyzed at a time. |
| NovaSeq 6000 (Illumina) |
Max output:3,000 Gb / flow cell Max paired end reads:10 billion reads/run Max read length:150 bp×2 (with S4 flowcell) The whole genome sequence of 60 individuals can be analyzed at a time. |
| HiSeq 2500 (Illumina) |
Max output:90 Gb / flow cell (Rapid Run Mode) Max paired end reads:300 million reads/run (Rapid Run Mode) Max read length:150 bp×2 (Rapid Run Mode) Installed when our project started in 2012, and is currently only used for small-scale analysis. |
| MiSeq (Illumina) |
Max output:15 Gb / flow cell Max paired end reads:2.5 million reads/run Max read length:300 bp×2 Used for metagenome analysis of microbiome and the quality control of sequencing libraries. |
| PromethION 24 (Oxford Nanopore Technology) |
Max output:~75 Gb /flow cell* Max read length:~100,000 bp** Long-read sequencer. Used for the structural variation analysis and de novo assembly. The performance depends on the protocol and the sample quality. *The performance under the protocol for JSV1 (Japanese Structural Variation) **The performance under the protocol for JG3 (Japanese Reference Genome) |
| Revio (PacBio) | Max output:100Gb/SMRT cell Max read length:20,000 bp Q20 reads: >99% Long-read sequencer. High quality reads as equivalent to short read sequencers can be obtained. |
Omics Analysis
The cutting-edge facility for omics analysis allows the analysis and quantification, to a high degree of precision, of the various metabolites and proteins that are contained within the blood and urine samples stored in the biobank facility. Three high-field and high-sensitive nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy system (800MHz and 600MHz) and various types of mass spectrometry system (LC-MS, GC-MS, etc.) have been installed to enable a wide variety of analysis to take place. Each system has an auto-sampler, allowing analyze several thousands of samples to be analyzed per year. The obtained data are then stored in the supercomputer system. Our study provides the standard omics information (types and quantity of metabolites and proteins) of Japanese people, which is useful for a wide range of medical treatment and research.


Equipment Configuration
| Model | Resonant frequency | Purpose of Use | Equipment |
| Bruker 800 NMR | 800MHz | Targeted metabolome analysis. | High Sensitivity Cryogenic Probe |
| Bruker 600 NMR | 600MHz | Comprehensive metabolome analysis. | Auto-Sample Changer |
| Model | Quantity | Purpose of Use | Equipment |
| Synapt G2-Si (Waters), QExactive (Thermo Fisher Scientific) | 3 | Comprehensive metabolome analysis. | Ultrahigh-speed Liquid Chromatograph |
| Xevo TQ-S (Waters), Xevo TQ-XS (Waters), TQ8040 (Shimadzu) |
5 | Targeted metabolome analysis. | Ultrahigh-speed Liquid Chromatograph, Gas Chromatograph |
| Orbitrap Fusion (Thermo Fisher Scientific) | 1 | Comprehensive metabolome analysis. Targeted and comprehensive proteome analysis. |
Ultrahigh-speed Liquid Chromatograph, Nano-LC |
Array Analysis
SNP genotyping using microarray techniques are performed in the facility designated for array analyses. Several types of microarray systems are used according to the purpose of each project Each system is equipped with a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) to record samples and reagents information, conditions of dispensing robots, and information regarding to process control. The microarray data are then sent to our supercomputer system where quality checks and genotype imputation are performed.
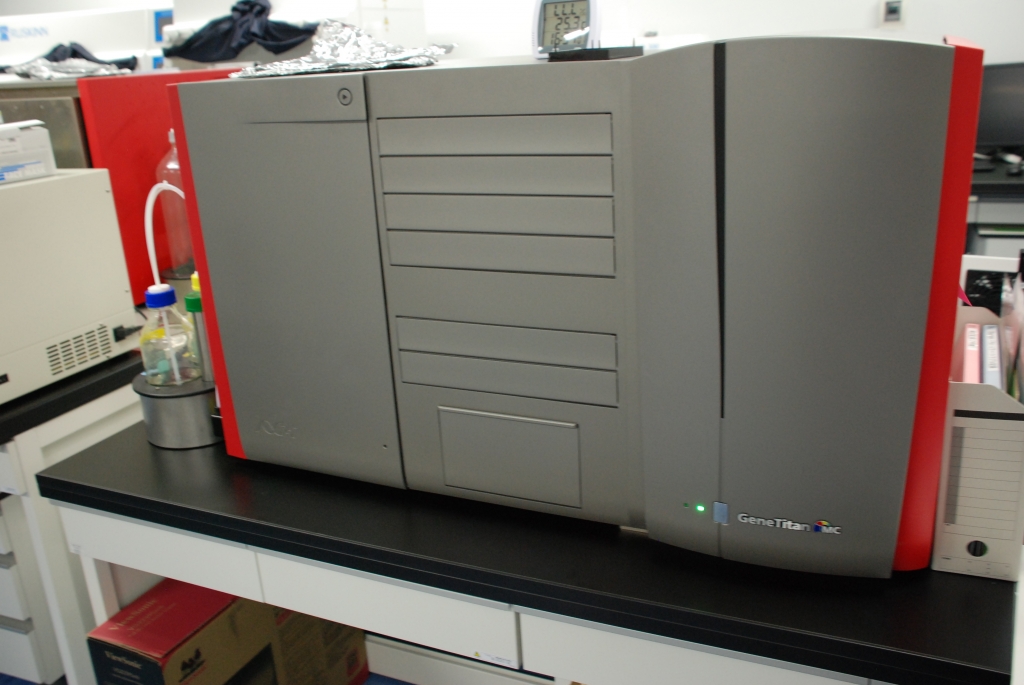
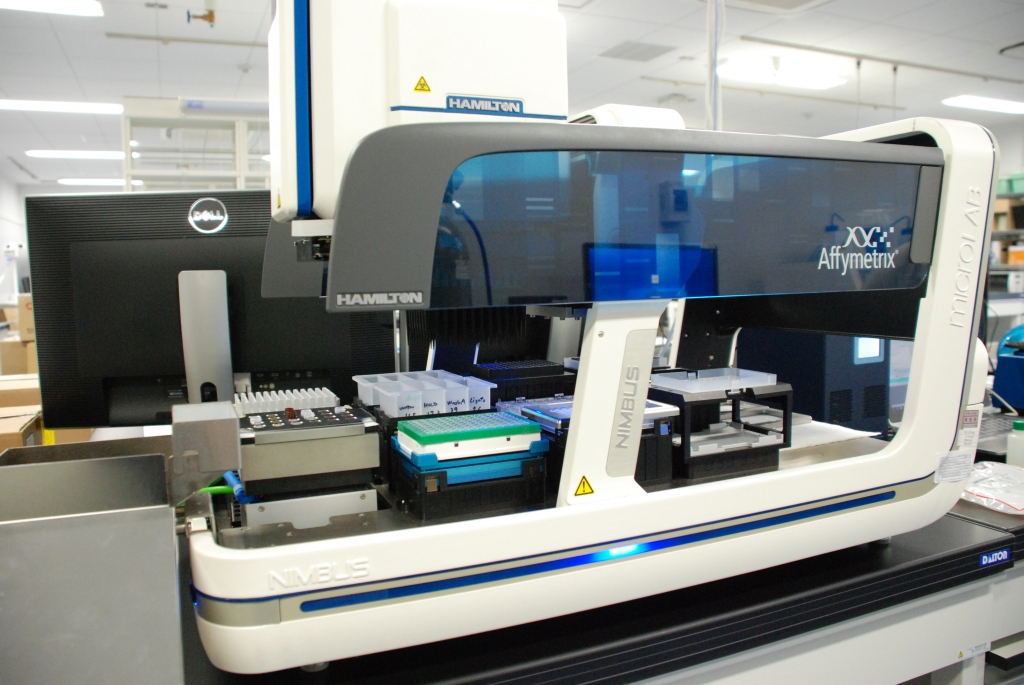


Equipment Configuration
| Model | Quantity | Feature |
| GeneTitanTM: Fully-automated hybridization and scanner system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) | 2 | Equipment for analyzing fully-customized arrays loaded with approximately 700,000 SNPs (Japonica Array®). With the standard specifications, 1 machine can obtain data from 384 specimens per week. |
| iSCAN scanner system (Illumina) | 2 | Equipment for analyzing BeadChip microarrays. Used to obtain data from Omni2.5 arrays, which are loaded with approximately 2.5 million SNPs. |
Clinical Biobank
As one of the facilities of INGEM, the clinical biobank operates along with the Tohoku University Hospital Personalized Medicine Center to collect precious biological specimens through medical care from the Tohoku University Hospital. Not only does it store liquid samples such as blood components, but also various types of other samples, including tissue specimens from surgery. All the biological specimens are anonymized and preserved at appropriate temperatures for future research.


Equipment Configuration
| Equipment | Quantity | Operating Temperature | Capacity |
| Ultra-low temperature freezer | 10 | -80 °C | Liquid samples: over 300,000 sample tubes (1 cc) |
| Tissue samples: over 40,000 sample cases |
Cryo-electron Microscopy
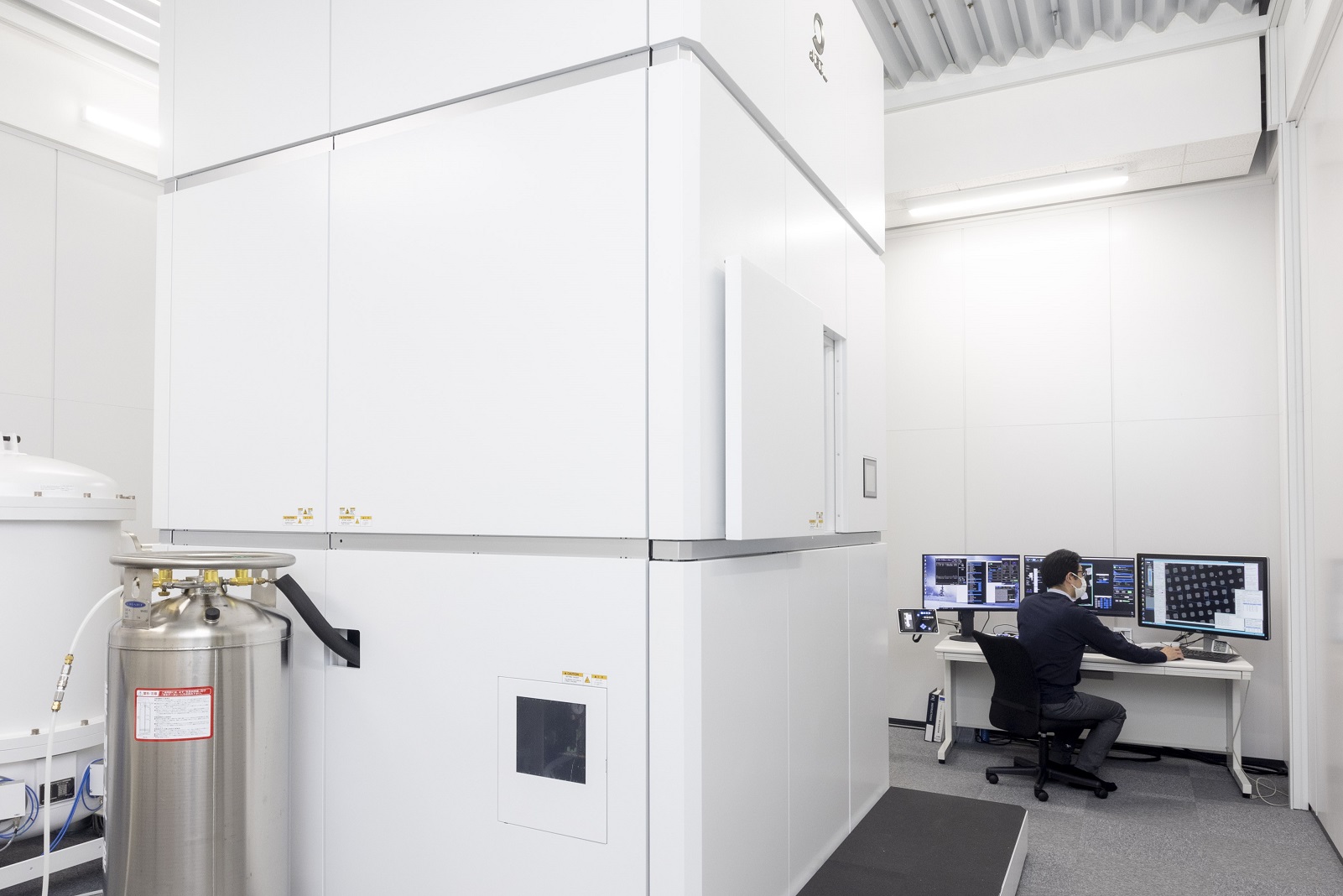
Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscope (CRYO ARM™ 300 II, JEOL Ltd.) and Cryogenic Focused Ion Beam Scanning Electron Microscope (JIB-4700F, JEOL Ltd.) are available for research in structural biology and cryo-electron tomography. Additionally, the ToMMo supercomputer is accessible for analyzing large datasets. These instruments are available not only to researchers at Tohoku University but also to those in companies and other research institutes, supporting investigations into disease mechanisms and drug discovery based on structural information.


About INGEM
In 2017, Tohoku University was selected as the first three Designated National Universities in Japan. The conferment of the Designated National University title is a recognition of the university's abilities to lead and shape global education and research. As a world-class research center and a leader of creativity and innovation. we have established a hub for next-generation medicine and founded INGEM as the organization that will play a central role within this hub.
In cooperation with ten departments within Tohoku University. We have created a structure that brings together our collective capabilities
Related Link
the Advanced Research Center for Innovations in Next-GEneration Medicine (INGEM)
