Collaborative research with OMRON HEALTHCARE Co., Ltd. (Multiple measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio strongly related home hypertension: TMM Cohort Study) was published in Hypertension Research
Collaborative research, an association between single-day or multi-day measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio and prevalence of hypertension, written by Assistant Professor Mana Kogure with OMRON HEALTHCARE Co., Ltd. (OMRON HEALTHCARE) was published in Hypertension Research.
Given that the guidelines by the Japanese Society of Hypertension recommend reduced salt (sodium) intake and increased potassium intake to prevent hypertension, the sodium-to-potassium ratio has recently been attracting attention. Further, an association between a high urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio and hypertension has also been reported in recent studies. It is reported that a 24-hour period of urine collection is the gold-standard method to accurately assess sodium intake, but obtaining measurement values on the spot in a short timeframe is difficult. However, recent studies show that multiple measurements of casual urine samples are highly correlated with the sodium-to-potassium ratio that is evaluated by the 24-hour urine collection. In addition, handy-sized urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio monitoring device (HEU-001F) that was developed by OMRON HEALTHCARE, it is possible to easily measure the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio in a short timeframe. Based on these findings, though no studies have evaluated the association between the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio and hypertension with long-term measurements in a large population, multiple measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio in casual urine samples may reveal a stronger correlation with hypertension.
The purpose of this study was to examine whether multiple measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio via casual urine strengthen the relationship between the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio and home-measured blood pressure better than a single measurement of the casual urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio. The subjects who participated in repeat assessment center-based survey during second period of the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project’s cohort study borrowed a home blood pressure monitoring device and a urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio monitoring device, then measured their urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio for 10 days. Hypertension was defined as a systolic blood pressure reading of ≥135 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure reading of ≥85 mmHg, or under treatment for hypertension. The urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio was divided into quartiles, and the average of each urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio from day 1 to day 10 and the odds ratios for the prevalence of hypertension were estimated, based on gender, age, body mass index (BMI), and drinking status. Of 3,273 participants results revealed that multiple measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio demonstrate a more sensitive association with hypertension than single measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio. These results suggest that multiple measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio are useful as an index to assess hypertension at home.
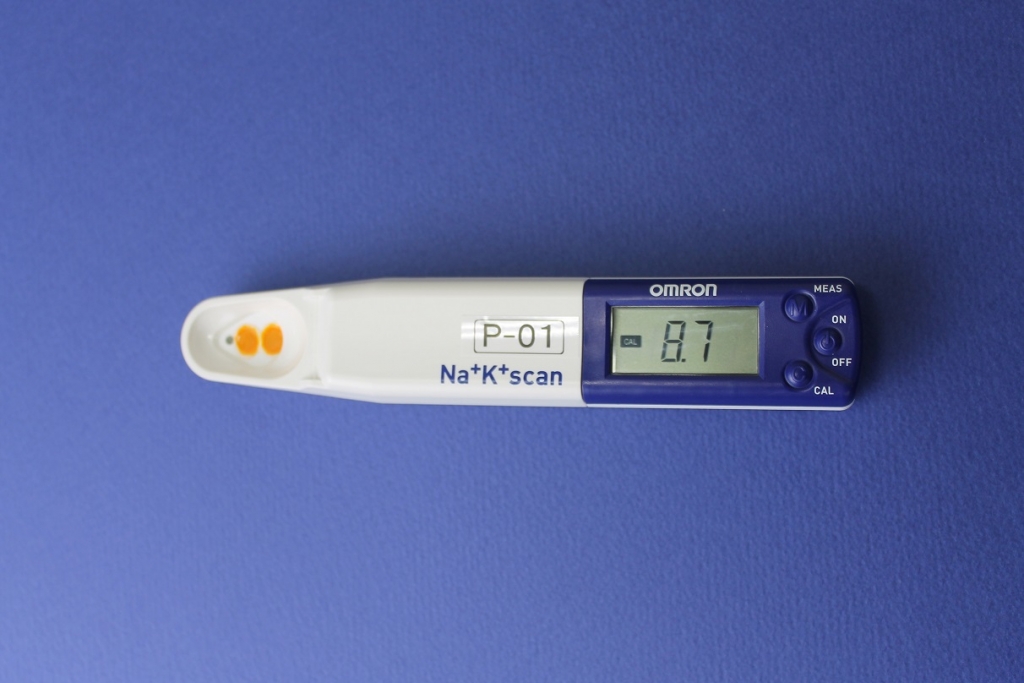
Handy-sized urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio monitoring device (HEU-001F, OMRON HEALTHCARE)
*This research is a collaborated with OMRON HEALTHCARE Co., Ltd.
Article information
Title: Multiple measurements of the urinary sodium-to-potassium ratio strongly related home hypertension: TMM Cohort Study
Authors: Mana Kogure, Takumi Hirata, Naoki Nakaya, Naho Tsuchiya, Tomohiro Nakamura, Akira Narita, Ken Miyagawa, Hiroshi Koshimizu, Taku Obara, Hirohito Metoki, Akira Uruno, Masahiro Kikuya, Junichi Sugawara, Shinichi Kuriyama, Ichiro Tsuji, Shigeo Kure & Atsushi Hozawa
Publishing journal: Hypertension Research
Published: 27 Sep 2019
DOI: 10.1038/s41440-019-0335-2
